Gum Therapy
For Healthy SmileGum diseases range from simple gum inflammation to serious disease that results in major damage to the soft tissue and bones that support the teeth. In the worst case, teeth are lost.
What causes gum disease?
Our mouth is full of bacteria.
These bacteria, along with mucus and other particles, constantly form a sticky,
colorless "plaque" on teeth.Brushing and flossing help get rid of plaque.
Plaque that is not removed can harden and form "calculus".
Brushing cannot clean “calculus”.
Only a professional cleaning by a dentist can remove calculus.
Gingivitis
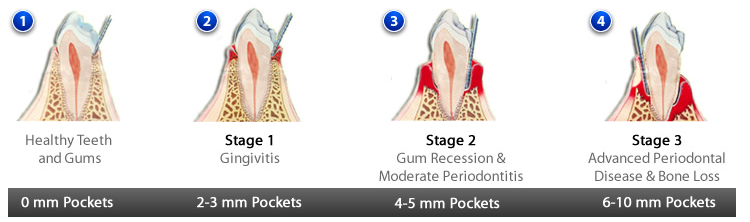
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease.
If plaque and calculus stay on teeth for a long period they can lead to gum disease.
The bacteria cause inflammation of the gums.
Can it be rectified ?
Daily Brushing.
Flossing.
Regular cleaning by a dentist.
Yes, of course! It can be easily reversed with
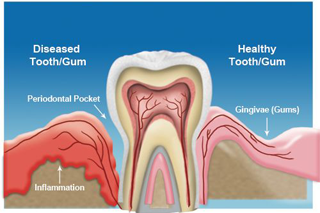
Periodontitis
When gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to "periodontitis" (which means "swelling
around the tooth").In periodontitis, gums pull away from the teeth and form spaces called "pockets" that become infected.
The body's immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line.
Bacterial toxins and the body's natural response to infection start to break down the bone and
connective tissue that hold teeth in place.If not treated, the bone, gums, and tissues that support the teeth are destroyed. The teeth may
eventually become loose and have to be removed.
Risk Factors
Smoking : Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors associated with the development of gum
diseases. Additionally, smoking can lower the chances of successful treatment.Hormonal changes in girls/women : These changes can make gums more sensitive. That in turn and
makes iteasier for gingivitis to develop.Diabetes : People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing infections, including gum diseases.
Other illnesses : Diseases like cancer or AIDS and their treatment can also negatively affect the health of
gums.Medications : Some medicine can reduce the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on the mouth.
Without enough saliva, the mouth is vulnerable to infections such as gum diseases. And some
medicines can cause abnormal overgrowth of the gum tissue.Genetic susceptibility : Some people are more prone to severe gum disease than others. Preventive
Dentistry

How do I know if I have gum disease?
Symptoms of gum disease include:
Bad breath.
Red or swollen gums.
Tender or bleeding gums.
Pain on chewing.
Loose teeth.
Sensitive teeth.
Receding gums.
Any of these symptoms may be a sign of a serious problem, which should be treated immediately by a dentist.
How is gum disease treated?
The main goal of treatment is to control the infection. The number and types of treatment will vary, depending on the extent of the gum disease.

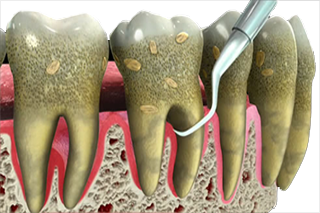
Deep Cleaning
The scale and root planning is one of the most important treatments which helps to fight against
gum disease.Scaling means scraping off the calculus from above and below the gum line.
Root planning gets rid of rough spots on the tooth root where the germs gather.
This treatment helps remove bacteria that contribute to the disease.
Surgical Treatments
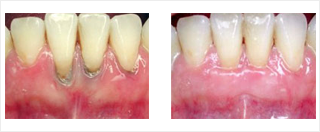
Flap Surgery
Surgery might be necessary if inflammation and deep pockets persist even after deep
cleaning and medications. This surgery involves lifting back the gums and removing the calculus.The gums are then sutured back in place.
After surgery the gums will heal and fit more tightly around the tooth.
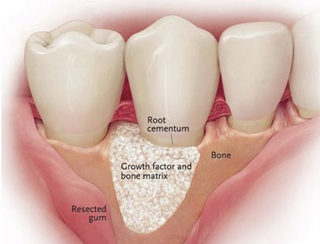
Bone and Tissue Grafts
In this, natural or synthetic bone is placed in the area of bone loss. This can help promote bone growth.
If gum tissue has been lost, the dentist may suggest a soft tissue graft.
This synthetic material or tissue is taken from another area of your mouth.
That is used to cover exposed tooth roots.
Do's
Rinse and wash your mouth with mouth wash on the day of Gum Surgery.
You can rinse gently every three hours with warm salt water also.
Keep your mouth as clean as possible which helps the healing process.
Stay on a liquid diet for the first two days after Gum treatment.
Dont's
Reduce physical activity for several hours following Gum Surgery.
Do not apply excessive tongue or cheek pressure on the treated area.
Do not brush or floss your teeth until instructed to do so.
If you smoke, we encourage you to stop smoking.


